When setting up a home CCTV system, the Field of View (FOV) is one of the most important factors to consider. It determines how much area your camera can monitor and directly impacts how effective your security setup will be. In this guide, we’ll explain everything you need to know about FOV, how it relates to lens sizes, and how to choose the best option for your specific needs.
What Is Field of View (FOV) in CCTV Cameras?
The Field of View (FOV) refers to the area captured by the CCTV camera’s lens, measured in degrees. Cameras with a wide FOV cover larger areas, while those with a narrow FOV focus on smaller, specific zones. The size of the lens determines the camera’s FOV, which can significantly affect the performance and purpose of the camera.
For example:
- A wider FOV is great for monitoring large spaces but may sacrifice detail.
- A narrower FOV focuses on specific areas with greater clarity but reduces the overall coverage.
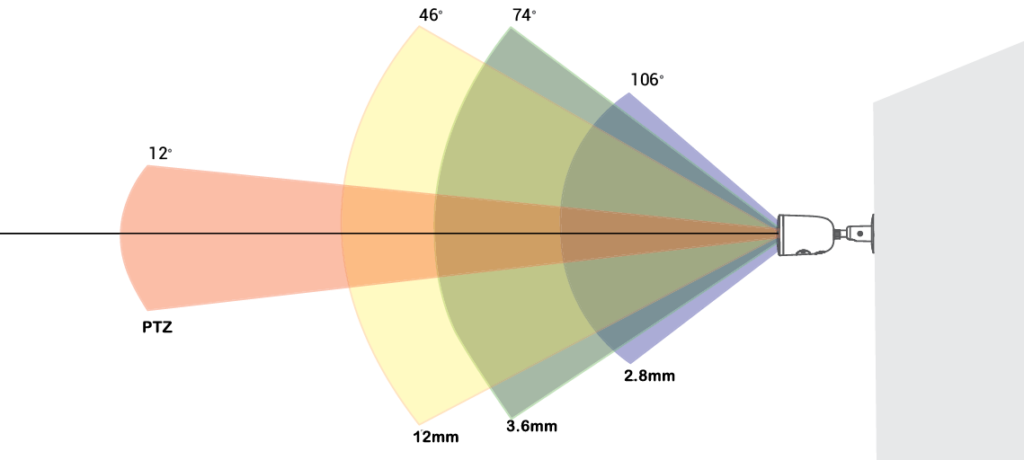
Lens Sizes and How They Affect FOV
The size of the lens is directly tied to the FOV of the camera. Different lens sizes are suitable for different purposes.
1. Wide-Angle Lenses (e.g., 2.8mm)
A 2.8mm lens with a wide field of view (approximately 100–120°) is ideal for open spaces where full-area coverage is critical:
- Example: Monitoring a front garden or driveway in a typical UK semi-detached house.
- Why It Works: It reduces blind spots, ensuring you capture movement in corners and along property boundaries.
- Potential Limitation: While it covers more area, objects at a distance (e.g., a car 20m away) may appear less detailed.
Technical Note:
Wide-angle lenses tend to introduce some barrel distortion at the edges of the image. This effect is negligible for general monitoring but could distort perspective in forensic investigations.
Best For:
- Monitoring open spaces where overall coverage is more important than fine details.
2. Standard Lenses (e.g., 3.6mm)
A 3.6mm lens provides a field of view of roughly 80–90°, comparable to the human eye’s perception.
- Example: Monitoring a back garden or main entryway.
- Why It Works: It offers a natural perspective and balance between area coverage and object detail, making it versatile.
- Ideal Distance: Typically, these lenses are effective for objects within 5–15 metres.
- Use Case in the UK: Perfect for capturing delivery drivers approaching your doorstep while keeping the entire path within view.
Best For:
- Homeowners looking for versatile CCTV coverage without compromising detail.
3. Narrow Lenses (e.g., 12mm)
A 12mm lens offers a much narrower FOV (about 25–30°), focusing on specific areas with exceptional detail.
- Example: Monitoring a narrow alley or a long driveway leading to a detached property.
- Why It Works: It allows clear identification of licence plates or facial details at a distance.
- Ideal Distance: Best for objects or activities located 20–50 metres from the camera.
Technical Note:
Narrow lenses often come with greater depth of field, ensuring objects far away remain sharp. However, they sacrifice peripheral coverage, which may leave nearby areas unmonitored.
Best For:
- Specific surveillance needs, such as monitoring a long driveway, corridor, or alleyway.
4. Zoom Lenses in PTZ Cameras
PTZ (Pan-Tilt-Zoom) cameras are highly versatile, allowing users to dynamically adjust the FOV based on real-time needs.
- Example: A PTZ camera installed on a large property or business estate can:
- Use a wide FOV during off-peak hours for general surveillance.
- Switch to a narrow FOV to zoom in on specific activities, such as identifying a visitor at the gate or tracking movement in a car park.
Advanced Features:
Modern PTZ cameras integrate with motion detection and AI analytics, automatically zooming in on suspicious activity while maintaining a wide overview.
Best For:
- Large outdoor areas where you may need to zoom in on details or track movement in real time.
Fixed Lens: A fixed camera focal length offers a set angular field of view (FOV) that cannot be adjusted by the user.
Varifocal Lens: A varifocal camera allows the user to manually adjust the focal length, usually through screws or dials on the camera. Some advanced models feature motorised varifocal lenses, enabling digital zoom and focal length adjustments via a smartphone app or NVR (network video recorder) without losing image clarity. These lenses provide greater flexibility and customisation to meet specific surveillance needs.
Overlap in Camera Coverage
For areas with complex layouts, such as L-shaped gardens or properties with multiple entry points, overlap between cameras with different FOVs can enhance security.
- Example: Use a wide-angle camera (2.8mm lens) for overall coverage of the garden, supplemented by a narrow-angle camera (12mm lens) focusing on the shed or tool storage area.
How to Choose the Right FOV for Your Needs
The best FOV depends on the area you’re monitoring and the level of detail required. Here’s a breakdown to help you decide:
1. Wide Areas
- Examples: front gardens, car parks, open-plan interiors.
- Recommendation: Choose a wide-angle lens (2.8mm) to minimise blind spots and cover the entire space.
2. Narrow Spaces
- Examples: corridors, alleys, or specific entry points.
- Recommendation: Opt for a narrower lens (12mm) to focus on the area without wasting coverage.
3. Balanced Monitoring
- Examples: entrances, mid-sized rooms, or general home security.
- Recommendation: A 3.6mm lens offers a balanced FOV, making it versatile for a range of applications.
4. Dynamic Areas
- Examples: large outdoor spaces or multi-zone properties.
- Recommendation: Invest in a PTZ camera with a zoom lens for adjustable FOV based on real-time needs.
Factoring the Camera Placement Height and Angle
The height and angle at which a camera is installed significantly impact the practical effectiveness of its FOV:
- Wide FOV:
- Ideal Height: 2.5–3 metres above ground for optimal coverage of a front garden or yard.
- Tilt Angle: A downward angle of about 30–40° reduces blind spots directly beneath the camera.
- Narrow FOV:
- Ideal Height: 3.5–4 metres for long-distance monitoring, such as driveways or alleys.
- Tilt Angle: Minimal tilt (10–20°) ensures objects farther away are captured clearly.
Which Type of Night Vision Works Best for FOV?
Night vision capabilities are critical for home security cameras, especially in low-light conditions. The choice of night vision also affects FOV.
→Know more about Night Vision CCTV Cameras for UK Home Security
1. Infrared (IR) Night Vision
- IR night vision provides black-and-white images in the dark.
- It’s invisible to the human eye, ensuring discreet operation.
- Ideal for areas where light pollution or disturbing neighbours is a concern.
Pros:
- No light pollution.
- Energy-efficient.
- Discreet operation.
Cons:
- Black-and-white footage may lack detail in some scenarios.
2. Full-Colour Night Vision (White LED)
- Full-colour night vision uses white LED lights to capture colour footage in the dark.
- It works like a small floodlight, making it more noticeable.
Pros:
- Provides colour footage, useful for identifying details like clothing or car colours.
Cons:
- Can disturb neighbours and contribute to light pollution.
- Higher energy consumption.
3. Smart Dual Light Technology
- Combines IR and full-colour night vision.
- Operates in IR mode by default but switches to white LED when motion is detected.
Pros:
- Energy-efficient and less invasive.
- Provides the benefits of both IR and full-colour modes.
Best For:
- Homeowners who want discreet surveillance with the flexibility of colour night vision when needed.

How FOV and Lens Size Impact CCTV Performance
- Reducing Blind Spots:
- Wider FOV reduces blind spots, but strategic placement is still crucial.
- Detail Clarity:
- Narrower FOV offers clearer details, making it better for identifying faces or licence plates.
- Energy Efficiency:
- Infrared cameras with wide FOV are more energy-efficient than full-colour options.
- Flexibility:
- PTZ cameras with adjustable zoom provide the flexibility to monitor multiple areas with varying FOV needs.
Combining AI Analytics with FOV
Many modern CCTV cameras use AI-powered analytics to enhance the effectiveness of their FOV.
- Example Features:
- Motion Detection: Triggers recording or alerts only when movement is detected within the FOV.
- Human/Vehicle Detection: Reduces false alarms by differentiating between people, vehicles, and environmental factors like animals or swaying trees.
- Line-Crossing Alerts: Monitors specific zones (e.g., a gate) within the FOV and alerts when breached.
Real-Life Example:
In a UK home with a 3.6mm lens camera covering the front entrance, AI analytics can alert the homeowner when a delivery driver crosses the front garden path while ignoring movement caused by pedestrians on the adjacent pavement.
Additional Notes for Accuracy
- Cameras with wider FOVs (e.g., 2.8mm) generally require higher resolution to maintain image clarity across the larger monitored area. For example, a 4K resolution camera will provide better wide-angle clarity than a 1080p camera.
- Narrower FOV cameras (e.g., 12mm) often work well with lower resolutions since the pixel density is concentrated on a smaller field.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing FOV
- Choosing a Wide-Angle Lens for Narrow Spaces
- This results in wasted coverage and insufficient detail.
- Using a Narrow Lens for Large Areas
- Can leave significant blind spots, reducing overall security.
- Overlooking the Need for Adjustability
- Fixed lenses may limit adaptability, whereas PTZ cameras can accommodate changing requirements.
FAQs About FOV and Lens Sizes
- Q: What FOV is best for a front garden?
A: A wide-angle lens (2.8mm) is ideal for covering large open spaces. - Q: Can I use a 12mm lens for indoor monitoring?
A: It’s only recommended for narrow spaces like long hallways. - Q: What’s the advantage of PTZ cameras?
A: They allow real-time FOV adjustments, making them suitable for dynamic environments.
Please contact us for any of your query and information needed. Thanks!



